NAME Konektibitatea eta interoperabilitate teknikoa IIoTren alorrean
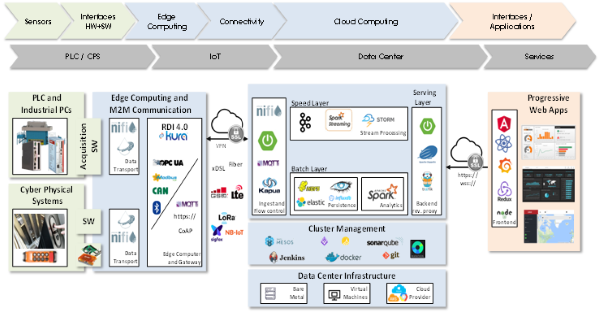
Aktibo logiko hau aplikazio transbertsalekoa da eta berarekin Fabrikazio Gehigarrian erabiltzen diren makinei/instalazioei eman nahi zaie Industry 4.0ko eremuan eskatzen den KONEKTIBITATE maila, batetik datuen garraioari lotutako alderdiei erantzuteko (bitateko fisikoak eta komunikazio protokoloak) eta, bestetik, Industry 4.0ra bideratutako plataformak osatzen dituzten modulu funtzionalen artean (sentsorizazioa, prozesamendu lokala, datuak sartzea, sekuentzien araberako prozesamendua, loteen araberako prozesamendua, datuak gordetzea, datuen analisia, datuen aurkezpena…) beharrezkoa den INTEROPERABILITATE TEKNIKOAri erantzuteko –APIen bidez (Application Program Interfaces)–. Interoperabilitate Teknikoa interoperabilitateari lotutako alderdi teknikoez baino ez da arduratzen, hala nola transmisio protokolez eta modulu funtzionalen arteko datu trukaketarako formatuez. Aktibo horrek Erreferentziako Arkitektura bat proposatzen du – plataformaren elementu guztien artean, hiru geruzatan egituratuta (Makina, Edge eta Lainoa), eta hiru geruza horietako batean emandako zerbitzuak eskatzen duen erantzun denbora (latentzia) eta segurtasun/pribatutasun maila bermatzera bereziki bideratuta. Arkitekturaren elastikotasunak aplikazioa errazten du Fabrikazio Gehigarriko kasuetan, hala nola hauetan: Monitorizazioa eta urrutiko kontrola, baldintzetan oinarritutako mantentze lanak, maila operatiboko erabaki hartzea automatizatua, kalitatearen on line kontrola, etab. Arkitektura horrek honi egiten dio erreferentzia: a) komunikazioko bitarteko fisikoak: Ethernet, xDSL, Wifi, Bluetooth/BLE, ZigBee, GPRS, 3G/4G, SIGFOX, LORA, NB-IoT, … , b) Komunikazio protokoloak: OPC-UA, Modbus, HTTPS, Web Services, REST, CoAP, MQTT, …, eta c) Modulu funtzionalak integratzeko APIak: NIFI, KURA, VAGRANT, ANSIBLE, APACHE SPARK, APACHE CASSANDRA, APACHE ZEPPELIN, ...
MOST OUTSTANDING EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
-
Cloud level connectivity
Infrastructure aimed at providing data ingestion, data storage, data analytics and data/information presentation, with a response time of the order of the second. It can communicate directly with the lower levels (Edge and Machine) using standard IIoT protocols. This infrastructure uses virtual machines and clusters installed on distributed servers to ensure the levels of availability demanded by the services. The enormous processing capacity available at this level allows to face self-learning services oriented to the modeling of the behavior of the machine, quality control on-line, unit traceability, automatic operative decision making, man-machine agile interfaces, etc.
-
Edge level connectivity
Infrastructure aimed at providing data ingestion and stream processing services, with a response time of the order of the tenth of a second. Communicates with the lower level (Machine) and above (Cloud) using standard IIoT protocols. This level implements Internet technologies in a near-machine environment, on a platform (hardware/software) dimensioned according to the privacy/security and latency requirements demanded by the node-resident services. NIFI and KURA are two of the relevant elements of the EDGE node. This node plays three basic tasks: a) Provide the degree of privacy/security and latency demanded at this level, b) implement services that require aggregated data from different machines, and c) serve as a gateway between the machine and the services available in the cloud. Services related to the dynamic reconfiguration of the production line, integration of 'plug-and-play' machines, 'quasi-real' time monitoring of the critical process variables, and intelligent maintenance based on conditions, are Just some of the typical services on this level.
-
Machine level connectivity
Wired Communication (UART, GPIO, SPI, I2C, CAN, USB,...) and wireless (IR, Bluetooth, Wifi, Zigbee, LPWAN,...) with industrial devices (CNCs, PLCs, transducers). Real-time local data processing capability. It can communicate directly with the upper levels (Edge and Cloud) using standard protocols in the IIoT field. Configuration, calibration, filtering/data adequacy and security-related decision-making services are typical at this level.
SERVICES OFFERED BY THE ASSET
Education, training, experimentation
Education, training and experimentation around the potential of the Reference Architecture in order to facilitate the process of creating infrastructure/platforms in the field of Additive Manufacturing. Aspects related to the implementation of the most relevant communication protocols (OPC-UA, REST, MQTT and Coap), and with the integration through APIs (technical interoperability) of the most popular functional modules: Data transport ( Nifi), Edge Computing (Kura), ingest and Data Control (KAPUA), real-time processing (spark steaming, Storm), batch processing (HDFS, Elastic, Influxdb, Spark Analytics), serving Layer (Apache Zepelin, Traefik), cluster Management (Mesos, Jenkins , Docker, Sonarcube, git), virtual machines (VirtualBox), cloud providers (AWS, Azure) will be considered.
IIoT Technical Interoperability
Technology transfer in Industry 4.0 scenarios through the joint development of monitoring, control and predictive maintenance projects in the context of Additive Manufacturing. It complements the Connectivity service with Technical Interoperability aspects -via APIs, in order to integrate the functional modules (software components) required by services.
Techinal connectivity
Technology Transfer (collaboration with the client) in the field of IIoT connectivity directed towards the implementation of infrastructures/platforms oriented to Additive Manufacturing. It focuses on Machine-Edge-Cloud connectivity aspects.
Technical Interoperability and Connectivity demonstrators
Presentation of Machine, Edge and Cloud level connectivity demonstrators based on the most widely used IIoT communication protocols, and the technical interoperability APIs of the most relevant functional modules in the field of Industry 4.0.
ENTITY MANAGING THE ASSET

Contact person:
Lorenzo Manero Peláez
lmanero@ikerlan.es