NAME SMART: Este activo recopila un sería de una serie de aplicaciones en distintos ámbitos que dotan a la máquina de unas prestaciones avanzadas y contribuyen a un diagnóstico y en algún caso actuación basados en inteligencia.
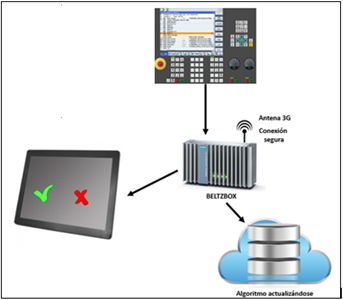
SMART: Este activo recopila un sería de una serie de aplicaciones en distintos ámbitos como son: Optimización térmica: Caracterización del comportamiento térmico de máquinas en base a ensayos en máquina sensorizada, modelización térmica de máquinas mediante MEF térmico avanzado, diseño de máquinas termoestables, monitorización y registro del comportamiento térmico de máquinas, desarrollo e implementación de funciones de control para compensación online de deformaciones térmicas. Funciones de control avanzadas: Desarrollo e integración de funciones de máquina avanzadas a partir de parámetros de control y sensores embebidos, para potenciación de las prestaciones del proceso, protección y seguridad de la máquina y ayuda a la operatividad para el usuario: equilibrado, autoajuste de ejes, protección de cabezales, detección de vibraciones anómalas, monitorización de proceso, etc. Integración de sensores en componentes críticos: Diseño e integración de componentes de máquina sensorizados, orientados a la mejora de prestaciones y seguridad de máquina y al soporte del proceso de fabricación: cabezales con acelerómetros integrados, husillos con sensores de temperatura y acelerómetros, estructuras de máquina con sensores de desplazamiento, etc. Desarrollo del HW, así como del SW necesario para ofrecer soluciones integrales, completamente integradas en la máquina y su control. Supervisión on-line de proceso de fabricación: información on-line, y en base a señales del CNC y sensores, sobre si un proceso de mecanizado está ocurriendo dentro de los parámetros admisibles, basándose en modelos de normalidad anteriormente definidos mediante el histórico de datos para una pieza/proceso en concreto. Optimización de vida de herramienta: predicción de la vida remanente de herramientas de corte para procesos de mecanizdo en base a la captación de señales del CNC y sensores, emitiendo un diagnóstico continuo del tiempo de uso remanente o el número de piezas que podrá mecanizar una herramienta. Control de calidad de proceso: Cámara de visión 3D utilizando la tecnología de luz estructurada integrada en la máquina. Gracias al SW de detección, localización y comparación se controla la calidad de la pieza terminada, pudiendo definir el usuario acciones correctivas. También se puede controlar antes del proceso la adecuación de la pieza inicial al CAD de la pieza objetivo. Estas aplicaciones dotan a la máquina de unas prestaciones avanzadas y contribuyen a un diagnóstico y en algún caso actuación basados en inteligencia.
FIELDS OF APPLICATION
Digitalization and Conectivity
MOST OUTSTANDING EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
-
CNC controls for the development of thermal deflection offsetting functions through the control of machine-tools.
CNC controls for the development of thermal deflection offsetting functions through the control of machine-tools.
-
Sensors for integration in machine components (accelerometers, thermocouples, LVDTs, etc.) and associated electronics.
Sensors for integration in machine components (accelerometers, thermocouples, LVDTs, etc.) and associated electronics.
-
Software for the calculation of thermal performance by finite elements: MSC MARC
Software for the calculation of thermal performance by finite elements: MSC MARC
-
Thermal testing measurement equipment: displacement, temperature, level sensors, etc.
Thermal testing measurement equipment: displacement, temperature, level sensors, etc.
-
Vibration acquisition and processing equipment
Vibration acquisition and processing equipment
SERVICES OFFERED BY THE ASSET
Advising
Advice for the implementation of solutions based on mono and/or multi-objective optimization algorithms for the improvement of processes, machines, supply chains, operator shift planning, maximization of efficiency and minimization of cost in industrial processes, etc.
Balance solution for machine-tool dividers
Development and implementation of balance solutions and protection of dividers based on integrated accelerometers.
Characterisation of the thermal performance of machines through testing
Characterisation of the thermal performance of machines through thermal and environmental testing of machine heating, performed on a sensorised machine to record its temperatures and deflections
Control functions to offset the machine’s thermal deflections
Development of mathematical models to offset machine deflections based on characterisation Design of control functions to offset the machine’s thermal deflections
Design of thermoset machines
Design of machines aimed at the optimisation of thermal performance, reducing heat spots, as well as structural deflections.
Design, integration and processing of sensorised machine-tool components
Design and integration of sensorised machine components to improve the machine features and safety and support the manufacturing process. Development of HW and the necessary SW to offer comprehensive solutions, fully integrated in the machine and their control.
Integration of camera in the machine for control of the initial part and CAD.
Development and integration testing of 3D computer vision systems in machines to control the suitability of the initial part.
Integration of camera in the machine for quality control
Development and integration testing of 3D computer vision systems in machines for quality control.
Modelling, characterisation and thermal optimisation of machines by finite elements
Thermal modelling of machines through calculation by finite elements. Simulation of thermal load and environmental machine heating to calculate the machine’s deflections. Sensibility study of the machine’s components to heat spots and thermal deflections. Proposal and simulation of design solutions for the optimisation of thermal performance and cushioning of the deflections.
Monitoring and protection of machine-tool heads
Monitoring and supervision of head vibrations through integrated accelerometer signals and the machine’s internal control signals to help the manufacturing process and to protect the head through foreseeing wear and tear or detection of collisions.
Optimisation of tool lifetime
Once the required process signals have been collected (CNC and/or sensors), they are analysed and wear models are generated for a certain operation. Then, when these operations are performed, the system informs on the estimated remaining life for a tool.
Research into manufacturing processes (machining) to generate models that enable their status to be controlled in real time.
Once the required process signals have been collected (CNC and/or sensors), they are analysed and normality models are generated for a certain operation. Subsequently, when these operations are performed, the system informs at a machine-level whether the process fulfils the pre-established normality thresholds.
Sensing of ball screws and signal processing
Integration of sensors in ball screws and processing of the signals acquired, along with the machine’s control parameters, to foresee failures and wear in the component.
ENTITY MANAGING THE ASSET

Contact person:
Karmele Florentino
karmele.florentino@tecnalia.com